Data Motion Acceleration
Abstract
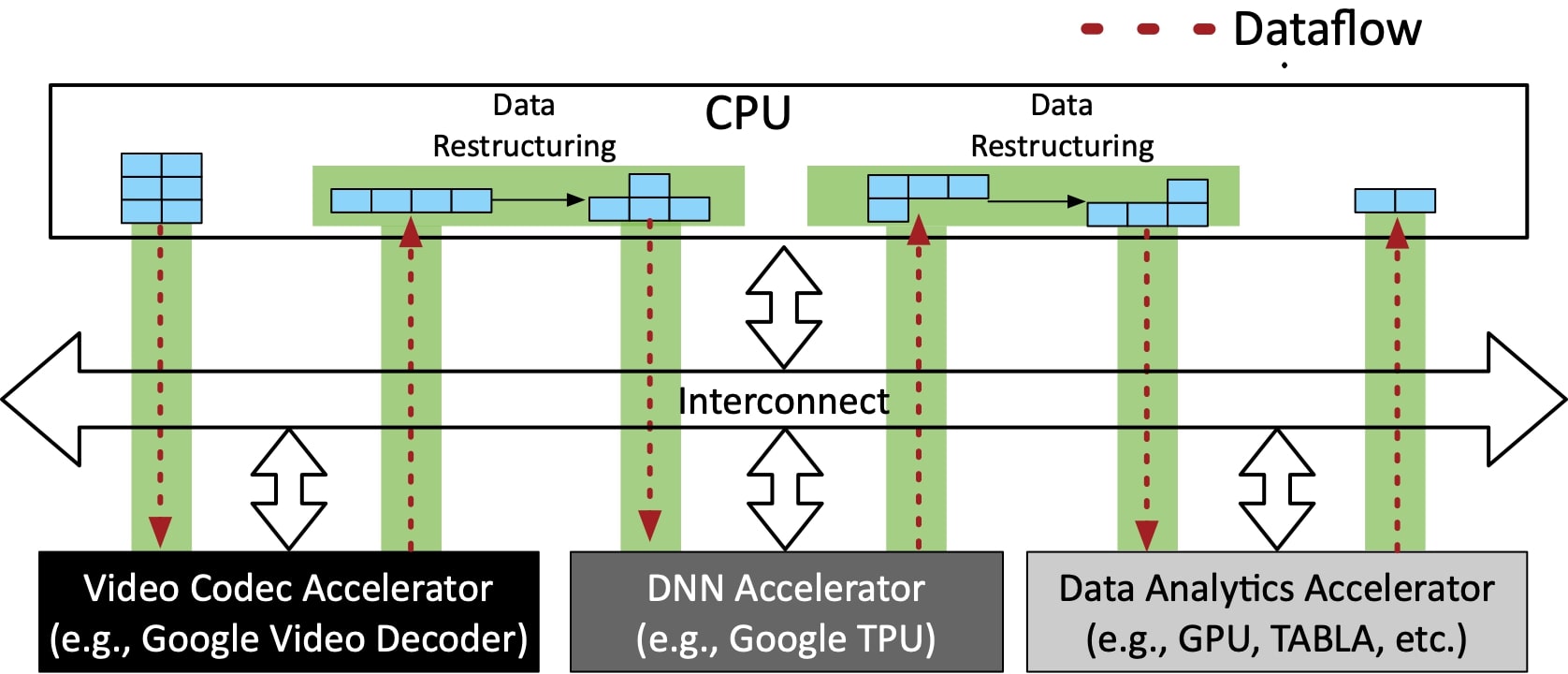
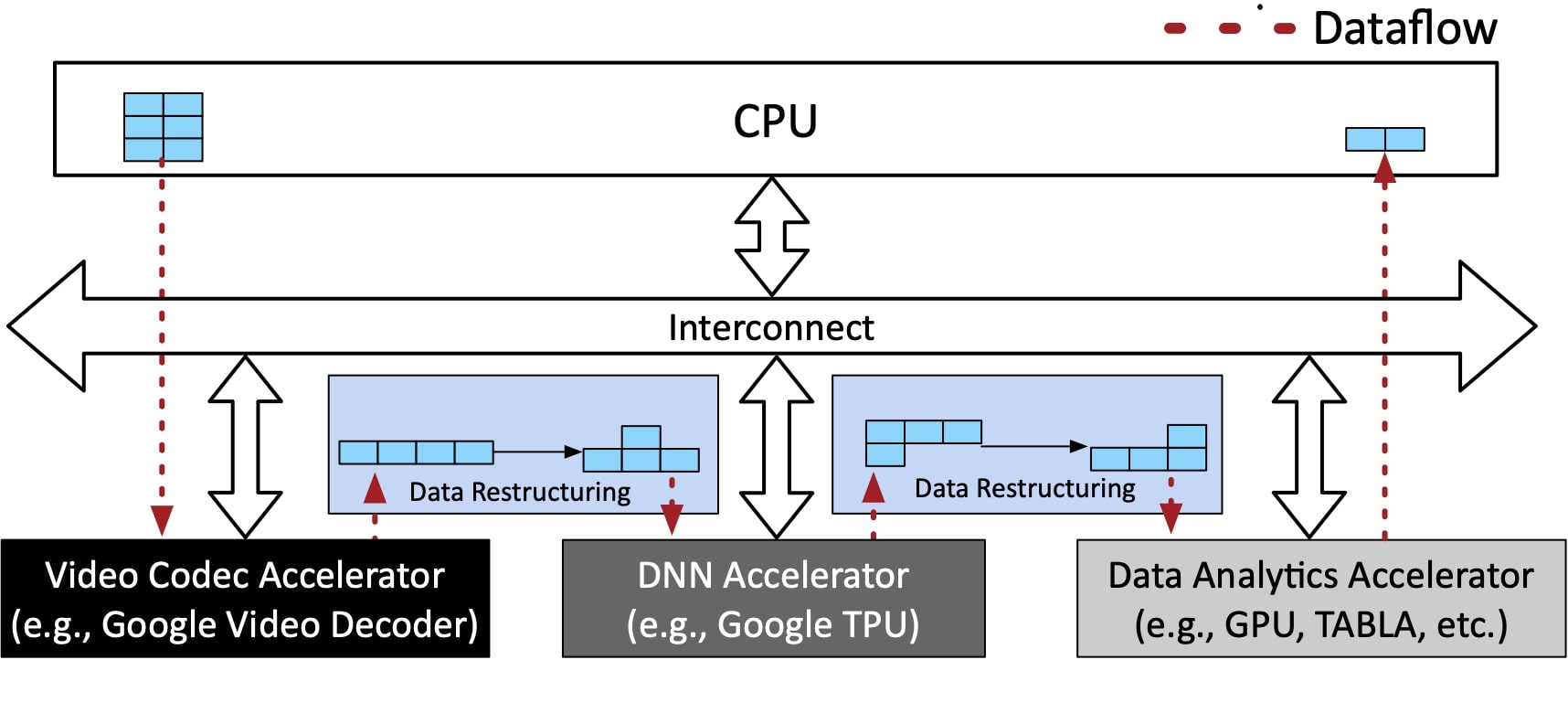
There has been an arms race for devising accelerators for deep learning in recent years. However, real-world applications are not only neural networks but often span across multiple domains, e.g., database queries, compression, encryption, video coding, signal processing, and traditional machine learning, which may or may not contain deep learning. The sole focus on this single domain is sub-optimal as it misses the potential to proliferate and promote cross-domain multi-acceleration as there is an opportunity to harness the power of chaining heterogeneous Domain- Specific Architectures (DSAs) in modern datacenter applications. However, there is a catch as the data motion overhead can outweigh the benefits from all these chained heterogeneous accelerators. We dub the data restructuring and communication overhead of executing a single application using a chain of accelerators as the data motion overhead.
In a stark contrast with most works on DSAs that deal with accelerating compute kernels, this work focuses on accelerating data motion within a chain of heterogeneous DSAs in a multi-accelerator datacenter. To that end, this project introduces Data Motion Acceleration (DMX) for (1) reducing data movement, (2) accelerating data restructuring, and (3) enabling interoperability between heterogeneous accelerators from different domains through a cross-stack hardware-software solution. The results with five end-to-end applications show that utilizing DMX offers up to 8.2x, 13.6x, and 5.2x improvement in latency, throughput, and energy efficiency in a multi-accelerator system, respectively.